Expectations and behavior of households in the sphere of supplementary education of children (based on results of surveys of schoolchildren’s parents concerning supplementary education of children and parents of children attending institutions for supplementary education of children, 2013)
%202015.jpg.(159x225x123).jpg) Full text in Russian (pdf) | No. 4 (86), 2015 Author: D.Filippova, S.Kosaretskij, B.Koupriyanov This bulletin presents the results of two surveys performed in 2013 in the framework of Monitoring of education markets and organizations: parents of schoolchildren attending supplementary studies and parents of children studying at education institutions for supplementary education of children. |
This bulletin presents the results of two surveys performed in 2013 in the framework of Monitoring of education markets and organizations: parents of schoolchildren attending supplementary studies and parents of children studying at education institutions for supplementary education of children.
The expectations of parents regarding the outcomes of supplementary education, the level of their satisfaction with received services, households’ expenditure on the supplementary education of children are considered. Special attention is paid to analyzing the scope and character of children’s involvement in education, including differences depending on the age of children, educational attainment, material well-being and place of residence of households.
The surveys of parents at schools and institutions for supplementary education of children allow us to characterize the behavior of households on the market of supplementary education services.
Supplementary education occupies a leading place in the structure of child’s time free from studying under a basic educational programme. Some of the children are involved in supplementary studies before going to school, but most of them do it at primary school. Supplementary education is considered by parents in the first place as a tool of common development and self-realization of children. Acquiring specific knowledge, including the improvement of knowledge under a basic school curriculum, is not a priority. In senior classes the scope of participation in supplementary education decreases and its character changes: the proportion of children attending education institutions for supplementary education of children and engaged in creative activities decreases; the proportion of those involved in supplementary education on the basis of a school, with tutors, increases; when choosing programmes the orientation towards educational outcomes increases; the proportion of children studying subjects on the school curriculum and foreign languages increases. Over two thirds of households are interested in increasing the scope of children’s supplementary studies. Almost half of children combine studying at education institutions for supplementary education of children and supplementary education at school. Some of them attend more than one hobby group (section) both at an education institution for supplementary education of children and at school.
Most popular kinds of studies are dances, fine arts and applied arts, music, sports, foreign languages. Less popular are science (research), designing, modeling, military-patriotic activities and tourism. One would notice a relation between a high level of mother’s educational attainment and the child’s attending arts circles, as well as a relation between the level of the household’s well-being and the child’s involvement in learning foreign languages additionally.
Among the reasons of choosing a place of receiving supplementary education, including education institutions for supplementary education, for the majority of parents the defining factor is what the child is wishing (particularly in well off households and among parents of senior pupils). The proximity from home is also an important factor, especially for parents of preschoolers and families where mothers have incomplete higher education. Free studies or a fee that one can afford to pay are of particular importance for less well off households and for parents of children who attend supplementary studies at municipal institutions for supplementary education. The main sources when choosingsupplementary studies, including studies at institutions for supplementary education, are friends and acquaintances, teachers and administration of institutions. The ability to give a child a sense of satisfaction, to generate interest and desire to be engaged in studying, to create a psychological comfort are the most significant requirements to supplementary education.
In more than half of the households children never interrupted the supplementary studies which they had started to attend. For those who had interrupted studying the reasons that were indicated most often were an inconvenience of attendance that had appeared and a change of children’s interests. The characteristics of conditions for receiving education at an institution (insufficient satisfaction with quality, qualification of the personnel, material base, salary growth) are seldom considered as reasons for interrupting studies.
For 47.2% of parents whose children attend education institutions for supplementary education or supplementary programmes are completely free. While as to parents surveyed at schools only 23.6% indicated that supplementary studies attended by their children (both at school and outside school) were free. The respondents who do not agree to pay for supplementary studies of their children in both surveys are more often less well off or mothers in those families do not have higher education.
An overwhelming majority of parents surveyed at education institutions for supplementary education of children and at schools are “probably satisfied” with the educational process.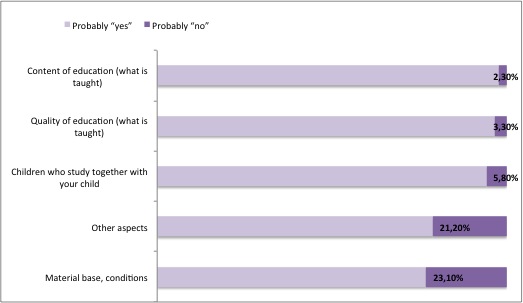
Fig. Parents’ satisfaction with some aspects of child’s studying at education institutions for supplementary education of children
(% of respondents who are parents of children attending institutions for supplementary education)
Prepared by S.Kosaretskij
Have you spotted a typo?
Highlight it, click Ctrl+Enter and send us a message. Thank you for your help!
To be used only for spelling or punctuation mistakes.